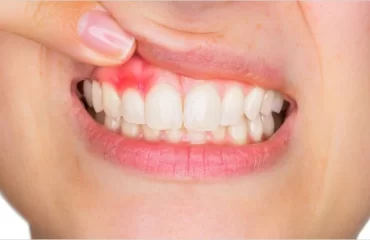
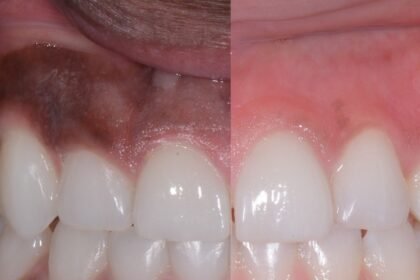
 GUM DIPIGMENTATION Gums play a crucial role in maintaining the overall oral health of an individual. While healthy gums are pink in color, some people may have darker gums that can affect their confidence and self-esteem. This condition is called hyperpigmentation of the gums or dark gums, and it can be caused by various factors. Fortunately, there are several treatments available that can help in depigmentation of dark gums.In this blog, we will discuss the causes of dark gums, depigmentation treatments, and prevention measures that can help you maintain healthy, pink gums.What is Depigmentation of Dark Gums?Depigmentation of dark gums, also known as gum bleaching or gum whitening, is a cosmetic procedure that lightens the color of the gums. The goal of this treatment is to improve the appearance of dark or discolored gums and give patients a more aesthetically pleasing smile.How does Depigmentation of Dark Gums Work?If you are unhappy with the appearance of your dark gums, there are several depigmentation treatments available that can help you achieve a brighter, more confident smileGum Bleaching – This treatment involves applying a bleaching agent to the gums, which helps to lighten the pigment in the gums. The bleaching agent can be applied either through a laser or chemical process.Gum Grafting – This treatment involves taking healthy gum tissue from another part of the mouth and grafting it onto the areas of the gums that are discolored. This treatment is more invasive than gum bleaching and requires a longer recovery time.Laser Gum Depigmentation – This treatment involves using a laser to remove the outer layer of pigmented gum tissue. This treatment is minimally invasive and has a short recovery time.Is Depigmentation of Dark Gums Safe?Depigmentation of dark gums is generally considered a safe procedure when performed by a qualified dental professional. However, as with any medical procedure, there are some risks involved. These may include bleeding, infection, or damage to surrounding teeth or tissues.Are there Any Side Effects of Depigmentation of Dark Gums?Like any medical procedure, depigmentation of dark gums can have some side effects. These may include bleeding, swelling, or pain in the treated area. Patients may also experience some sensitivity in the teeth or gums following the procedure. In rare cases, depigmentation of dark gums can lead to infection or damage to the surrounding teeth or tissues. However, most patients are able to resume normal activities within a few days of the procedure.What are the Best Depigmentation of Dark Gums Treatments?As mentioned earlier, there are a few different methods used to depigment dark gums. The best treatment for you will depend on a number of factors, including the severity of the discoloration and your individual needs and preferences. Laser gum depigmentation is a popular choice due to its effectiveness and minimal side effects.Chemical depigmentation may be a good option for patients with less severe discoloration. It’s important to discuss your options with a qualified dental professional to determine the best course of treatment for your individual needs.How long does Depigmentation of Dark Gums take to Heal?The healing time for depigmentation of dark gums can vary depending on the method used to perform the procedure. Laser gum depigmentation typically involves a shorter recovery time than chemical or surgical depigmentation. Patients may experience some swelling or discomfort in the treated area for a few days following the procedure. It’s important to follow your dentist’s instructions for post-operative care to ensure proper healing.Can Depigmentation of Dark Gums be Done at Home?While there are some over-the-counter products marketed for depigmentation of dark gums, it’s not recommended to attempt this procedure at home. Depigmentation of dark gums is a medical procedure that should only be performed by a qualified dental professional. Attempting to bleach or whiten the gums at home can result in serious damage to the gums or teeth.Causes of Dark Gums
GUM DIPIGMENTATION Gums play a crucial role in maintaining the overall oral health of an individual. While healthy gums are pink in color, some people may have darker gums that can affect their confidence and self-esteem. This condition is called hyperpigmentation of the gums or dark gums, and it can be caused by various factors. Fortunately, there are several treatments available that can help in depigmentation of dark gums.In this blog, we will discuss the causes of dark gums, depigmentation treatments, and prevention measures that can help you maintain healthy, pink gums.What is Depigmentation of Dark Gums?Depigmentation of dark gums, also known as gum bleaching or gum whitening, is a cosmetic procedure that lightens the color of the gums. The goal of this treatment is to improve the appearance of dark or discolored gums and give patients a more aesthetically pleasing smile.How does Depigmentation of Dark Gums Work?If you are unhappy with the appearance of your dark gums, there are several depigmentation treatments available that can help you achieve a brighter, more confident smileGum Bleaching – This treatment involves applying a bleaching agent to the gums, which helps to lighten the pigment in the gums. The bleaching agent can be applied either through a laser or chemical process.Gum Grafting – This treatment involves taking healthy gum tissue from another part of the mouth and grafting it onto the areas of the gums that are discolored. This treatment is more invasive than gum bleaching and requires a longer recovery time.Laser Gum Depigmentation – This treatment involves using a laser to remove the outer layer of pigmented gum tissue. This treatment is minimally invasive and has a short recovery time.Is Depigmentation of Dark Gums Safe?Depigmentation of dark gums is generally considered a safe procedure when performed by a qualified dental professional. However, as with any medical procedure, there are some risks involved. These may include bleeding, infection, or damage to surrounding teeth or tissues.Are there Any Side Effects of Depigmentation of Dark Gums?Like any medical procedure, depigmentation of dark gums can have some side effects. These may include bleeding, swelling, or pain in the treated area. Patients may also experience some sensitivity in the teeth or gums following the procedure. In rare cases, depigmentation of dark gums can lead to infection or damage to the surrounding teeth or tissues. However, most patients are able to resume normal activities within a few days of the procedure.What are the Best Depigmentation of Dark Gums Treatments?As mentioned earlier, there are a few different methods used to depigment dark gums. The best treatment for you will depend on a number of factors, including the severity of the discoloration and your individual needs and preferences. Laser gum depigmentation is a popular choice due to its effectiveness and minimal side effects.Chemical depigmentation may be a good option for patients with less severe discoloration. It’s important to discuss your options with a qualified dental professional to determine the best course of treatment for your individual needs.How long does Depigmentation of Dark Gums take to Heal?The healing time for depigmentation of dark gums can vary depending on the method used to perform the procedure. Laser gum depigmentation typically involves a shorter recovery time than chemical or surgical depigmentation. Patients may experience some swelling or discomfort in the treated area for a few days following the procedure. It’s important to follow your dentist’s instructions for post-operative care to ensure proper healing.Can Depigmentation of Dark Gums be Done at Home?While there are some over-the-counter products marketed for depigmentation of dark gums, it’s not recommended to attempt this procedure at home. Depigmentation of dark gums is a medical procedure that should only be performed by a qualified dental professional. Attempting to bleach or whiten the gums at home can result in serious damage to the gums or teeth.Causes of Dark Gums- Genetics– Genetics plays a significant role in the color of your gums. Some people may be born with naturally darker gums, which is usually nothing to worry about.
- Ethnicity – People of certain ethnicities, such as people of African, Asian, or Middle Eastern descent, are more prone to having darker gums due to the natural pigmentation of their skin.
- Smoking – Smoking tobacco products can cause staining of the teeth and gums, leading to dark gums.
- Medications– Certain medications like minocycline, an antibiotic, can cause gum discoloration as a side effect.
- Medical Conditions– Some medical conditions like gum disease, oral cancer, and chronic inflammatory conditions can cause dark gums.
- Brushing and Flossing– Brushing and flossing your teeth twice a day can help to remove plaque buildup and prevent gum disease, which can lead to dark gums.
- Regular Dental Checkups– Regular dental checkups can help to detect and treat gum disease in its early stages, preventing it from progressing and causing dark gums.
- Quitting Smoking– Quitting smoking can help to prevent staining of the teeth and gums, leading to a brighter, healthier smile.
- Proper Nutrition– Eating a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help to promote healthy gums and prevent gum disease.
- Using Natural Remedies– There are several natural remedies that can help to promote healthy gums, such as oil pulling, saltwater rinses, and aloe vera.
- Longevity of results
- Reduced hyper-pigmentation recurrence
- Laser therapy targets hyperpigmentation in gums.
- Suitable for various types of pigmentation, including patchy areas.
- Special consideration is needed for darker skin to avoid damage.
- Traditional treatments are available for surface pigment concerns.
- Enhanced smiles boost satisfaction.
- Dental clinics recognize the advantages of lasers for aesthetic results.