ALARMING SIGNS for ORAL HEALTH and ways to Prevent or Treat them Certainly, there are some ALARMING SIGNS to watch out for in your oral health, what they could mean, and ways to prevent or treat them:
ALARMING SIGNS for ORAL HEALTH and ways to Prevent or Treat them Certainly, there are some ALARMING SIGNS to watch out for in your oral health, what they could mean, and ways to prevent or treat them: - PERSISTENT TOOTHACHE:
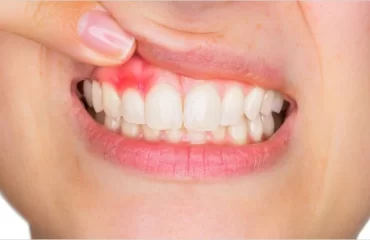
- BLEEDING GUMS:
- SWOLLEN OR PAINFUL GUMS:
- TOOTH SENSITIVITY:
- LOOSE TEETH:
- CHANGES IN BITE OR TOOTH ALIGNMENT:
- PAIN OR DISCOMFORT IN THE JAW (TMJ PAIN):
- MOUTH SORES:
- ORAL LUMPS OR GROWTHS: